بررسی نشانگرهای زیستی اختلال دوقطبی با استفاده از روشهای یادگیری بدون نظارت
کد: G-1975
نویسندگان: Maryam Hosseinpour ℗, Shahram Teimourian *, Zohre Moattar Husseini
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: آنالیز دادگان اومیکس
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
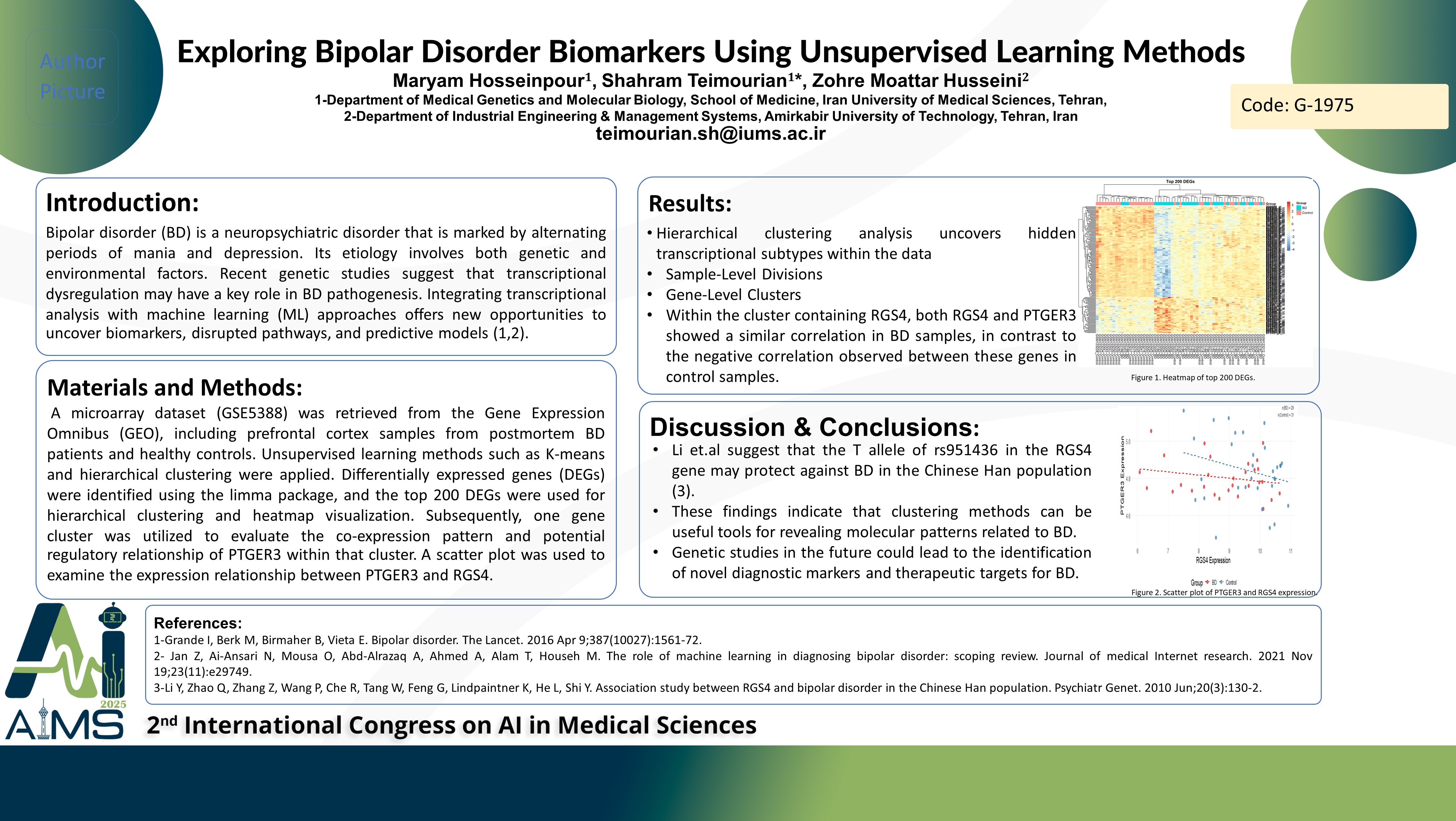
Background and aims: Bipolar disorder (BD) is a neuropsychiatric disorder that is marked by alternating periods of mania and depression. BD has been perceived as a multifactorial disorder, with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to its etiology. Recent genetic studies suggest that transcriptional dysregulation may have a key role in BD pathogenesis. Transcriptional analysis provides a powerful approach to understanding the molecular mechanism of this disease. Machine Learning (ML) techniques have also enhanced the ability to analyze complicated genetic data to discover new biomarkers, predictive models, and disrupted pathways for BD. The present study aims to explore the integration of ML approaches in genetic and transcriptomic research to improve the understanding of BD mechanisms. Method: In this study, a brief review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications in BD research, particularly on genetic analyses, was first conducted. Next, we retrieved a microarray dataset from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) GSE5388, comprising prefrontal cortex samples from postmortem BD patients and healthy controls. The data were analyzed using unsupervised learning algorithms of K-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, and statistics to identify the unknown patterns of gene expression. Finally, two genes, PTGER3 and FOS, were compared within each cluster using statistical analysis to ascertain whether they are implicated in BD pathophysiology. Results: The literature review highlighted the rising importance of AI in BD research, particularly in early diagnosis, treatment response prediction, and biomarker discovery. In our study, clustering of gene expression data revealed hidden patterns, with distinct transcriptional profiles dividing into biologically meaningful classes. Markedly, two genes, PTGER3 and FOS, within the clusters had a significant association in their expression patterns, suggesting their potential involvement in BD pathophysiology. Conclusion: These findings indicate that clustering methods can be useful tools for revealing molecular patterns related to BD. Genetic studies in the future could lead to the identification of novel diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for BD.
کلمات کلیدی
Bipolar-Disorder, Machine-Learning, Artificial-Intelligence, PTGER3