شخصیسازی پچ های میکرونیدل مبتنی بر هوش مصنوعی برای بهینهسازی درمان اسکار آکنه: یک مرور سیستماتیک
کد: G-1966
نویسندگان: Atefeh Mehdizadeh Shahsavar *, Anita Mousakhani ℗, Goli Osloub, Arefeh Mehdizadeh Shahsavar, Arastou Ghahremanzadeh, Yousef Javadzadeh
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: هوش مصنوعی و صنعت دارویی
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
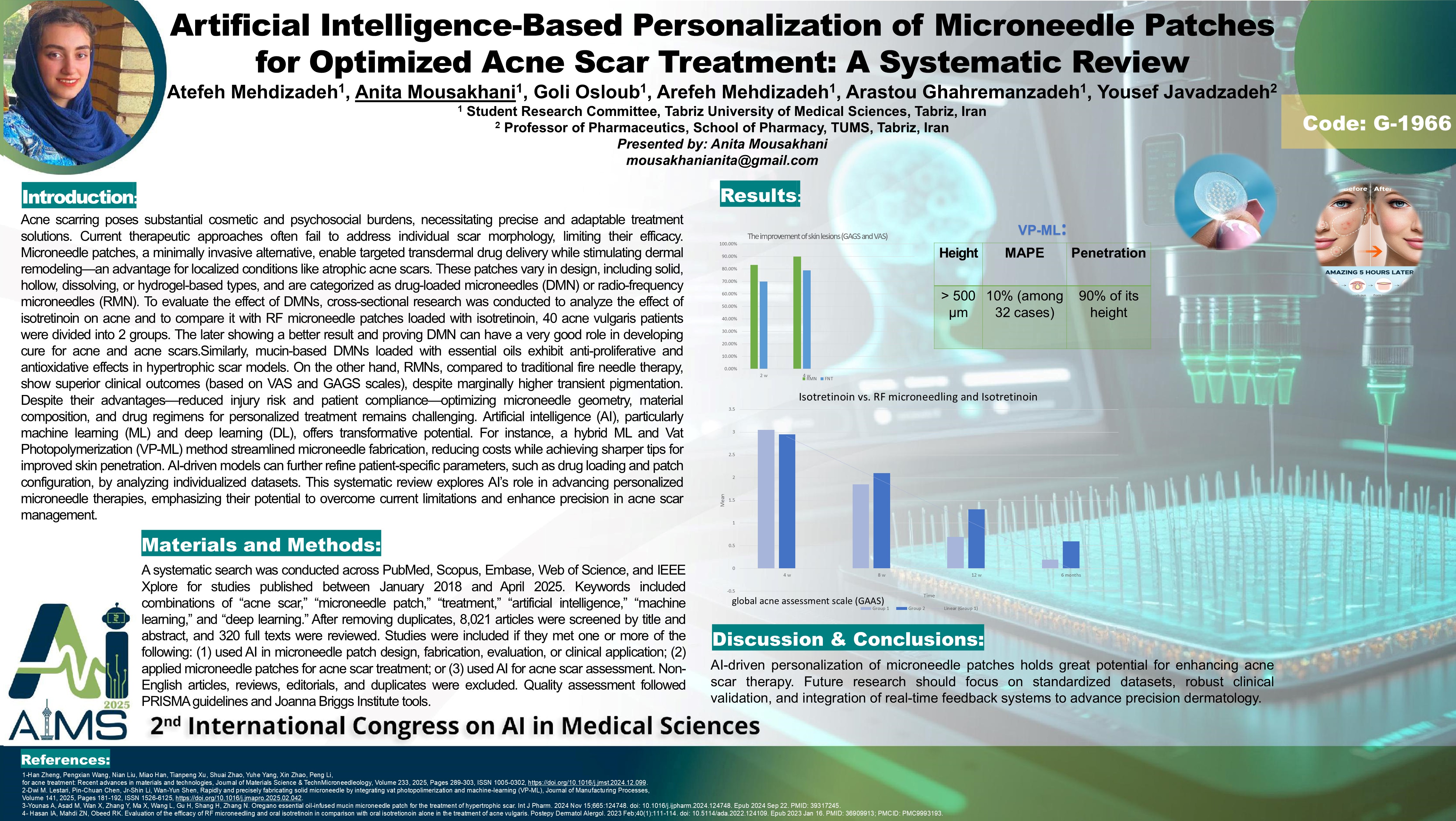
Background: Acne scarring presents significant cosmetic and psychosocial challenges. Current treatments often lack precision and adaptability to individual scar patterns. Microneedle patches offer a minimally invasive method for targeted transdermal drug delivery, and their inherent ability to stimulate dermal remodeling makes them particularly suitable for treating localized dermal conditions like atrophic acne scars. However, optimizing their design and therapeutic protocols to accommodate individual characteristics remains complex. Artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), offers promising avenues for personalizing microneedle geometry, material composition, drug loading, and treatment parameters based on patient-specific data. Methods: A systematic search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, and IEEE Xplore for studies published between January 2018 and April 2025. Keywords included combinations of “acne scar,” “microneedle patch,” “treatment,” “artificial intelligence,” “machine learning,” and “deep learning.” After removing duplicates, 8,000 articles were screened by title and abstract, and 320 full texts were reviewed. Studies were included if they met one or more of the following: (1) used AI in microneedle patch design, fabrication, evaluation, or clinical application; (2) applied microneedle patches for acne scar treatment; or (3) used AI for acne scar assessment. Non-English articles, reviews, editorials, and duplicates were excluded. Quality assessment followed PRISMA guidelines and Joanna Briggs Institute tools. Findings: Of the 320 articles assessed, 48 met inclusion criteria. AI applications were categorized into four main areas: (1) Design optimization using Bayesian and neural network models to improve dimensional precision; (2) Material selection using supervised learning to balance mechanical strength and solubility; (3) Drug release modeling via convolutional neural networks (CNNs), enhancing transdermal delivery by up to 30%; (4) Clinical evaluation through deep CNNs for acne scar grading, with reported sensitivity and specificity between 0.85 and 0.92. AI-enhanced personalization improved reproducibility, drug delivery efficiency, and response prediction. However, limited sample sizes and lack of standardized validation remain obstacles. Conclusion: AI-driven personalization of microneedle patches holds great potential for enhancing acne scar therapy. Future research should focus on standardized datasets, robust clinical validation, and integration of real-time feedback systems to advance precision dermatology.
کلمات کلیدی
Acne,Scars,Microneedle,Patches,Artificial Intelligence,Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Personalization