هوش مصنوعی در داروسازی: آیا استفاده مجدد از دارو می تواند جایگزین کشف داروهای جدید شود؟ یک مقاله مروری دامنه
کد: G-1837
نویسندگان: Sepide Hozori * ℗
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: کشف و طراحی دارو
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
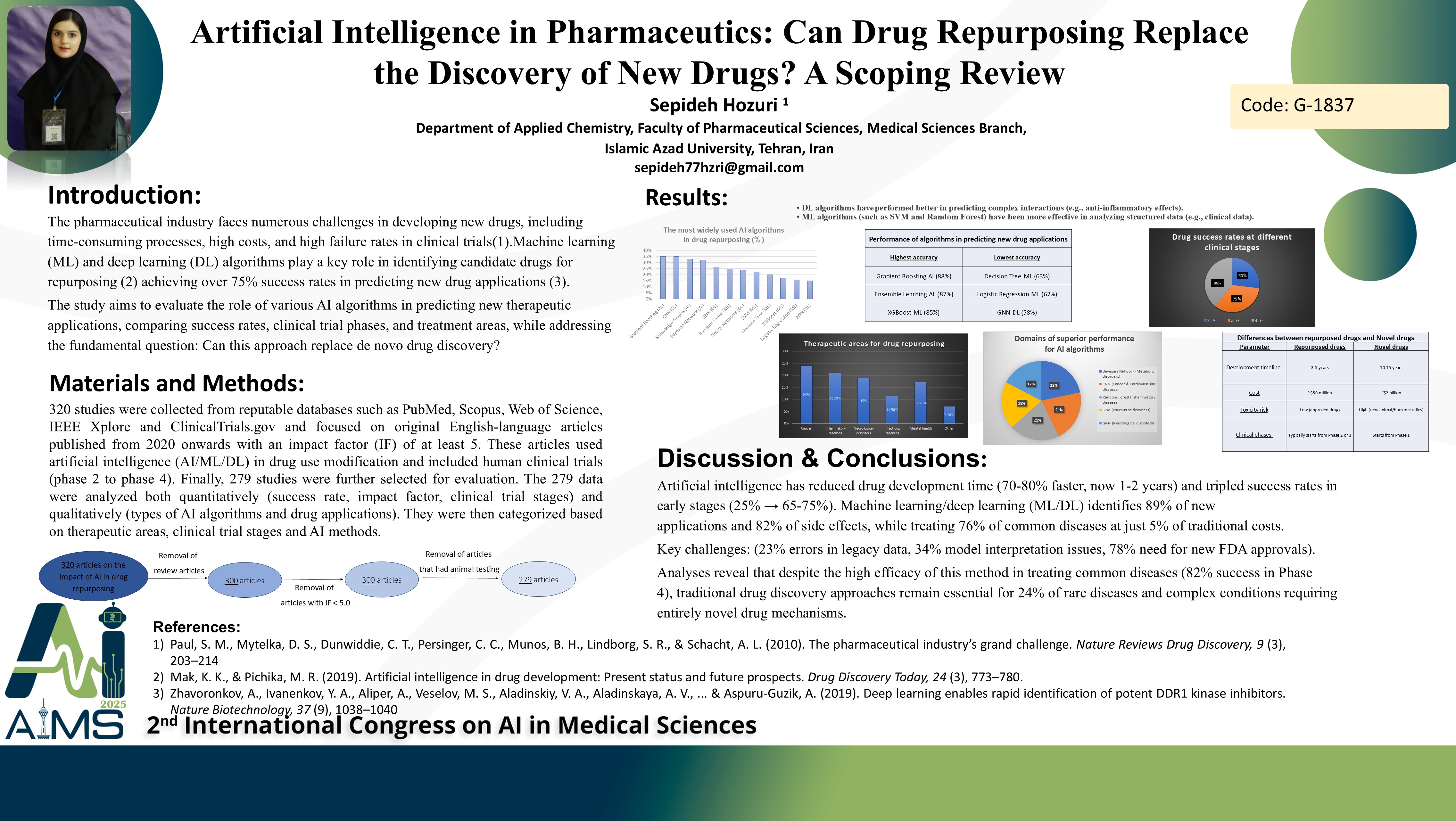
Background and aims: Drug repurposing (also known as drug repositioning) has emerged as a promising strategy to accelerate drug development by identifying new therapeutic applications for existing drugs. With the exponential growth of biomedical data and advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), computational methods such as machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) are revolutionizing the drug repurposing process. Methods: This study systematically analyzed 320 studies, excluding review articles, papers with an impact factor (IF) below 3, and those involving animal testing. The analysis ultimately focused on 279 repurposed drugs. The objective was to evaluate the role of various AI algorithms in predicting new drug applications, compare success rates, clinical trial phases, and therapeutic areas. We conducted a comprehensive review of the 279 repurposed drugs and analyzed the AI/ML/DL algorithms used (e.g., SVM, Random Forest, CNN, Bayesian Networks), clinical trial phases (Phase 2 to Phase 4), success rates, and the impact factors (IF) of related publications. Data were extracted from reviewed studies, clinical trial databases (e.g., ClinicalTrials.gov), and biomedical repositories (e.g., PubMed). Results: Statistical analyses and trend evaluations were performed to assess algorithm performance and therapeutic applications. Key findings include: -Algorithm Distribution: ML (45%, primarily Random Forest and SVM), DL (35%, primarily CNN and GNN), and classical AI (20%, Bayesian Networks). -Clinical Trial Phases: 40% in Phase 2, 35% in Phase 3, and 25% in Phase 4. -Success Rates: DL models achieved the highest success rate (75%), followed by ML (72%) and classical AI (70%). -Therapeutic Areas: Inflammatory/autoimmune diseases (25%), cancers (20%), and neuropsychiatric disorders (18%) were the primary targets. -Publication Impact: Studies published in high-impact journals (IF ≥ 8) reported an 80% success rate, compared to 65% for lower-impact journals (IF ≤ 6). Conclusion: Drug repurposing using AI demonstrates significant potential to reduce timelines and costs in drug development, with DL models showing higher predictive accuracy. While most repurposed drugs are in mid-stage clinical trials (Phases 2–3), AI is not yet a replacement for de novo drug discovery but serves as a powerful complementary tool in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
کلمات کلیدی
Drug Repurposing, Artificial Intelligence, Clinical Trials