تشخیص زخم معده در تصاویر آندوسکوپی با استفاده از هوش مصنوعی: یک مرور سیستماتیک و متاآنالیز دقت آزمونهای تشخیصی
کد: G-1772
نویسندگان: Behrad Eftekhari ℗, Anita Khalili, Ervin Zadgari, Saeed Ghaffari, Soheil Hassanipour *
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: پردازش تصاویر پزشکی
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
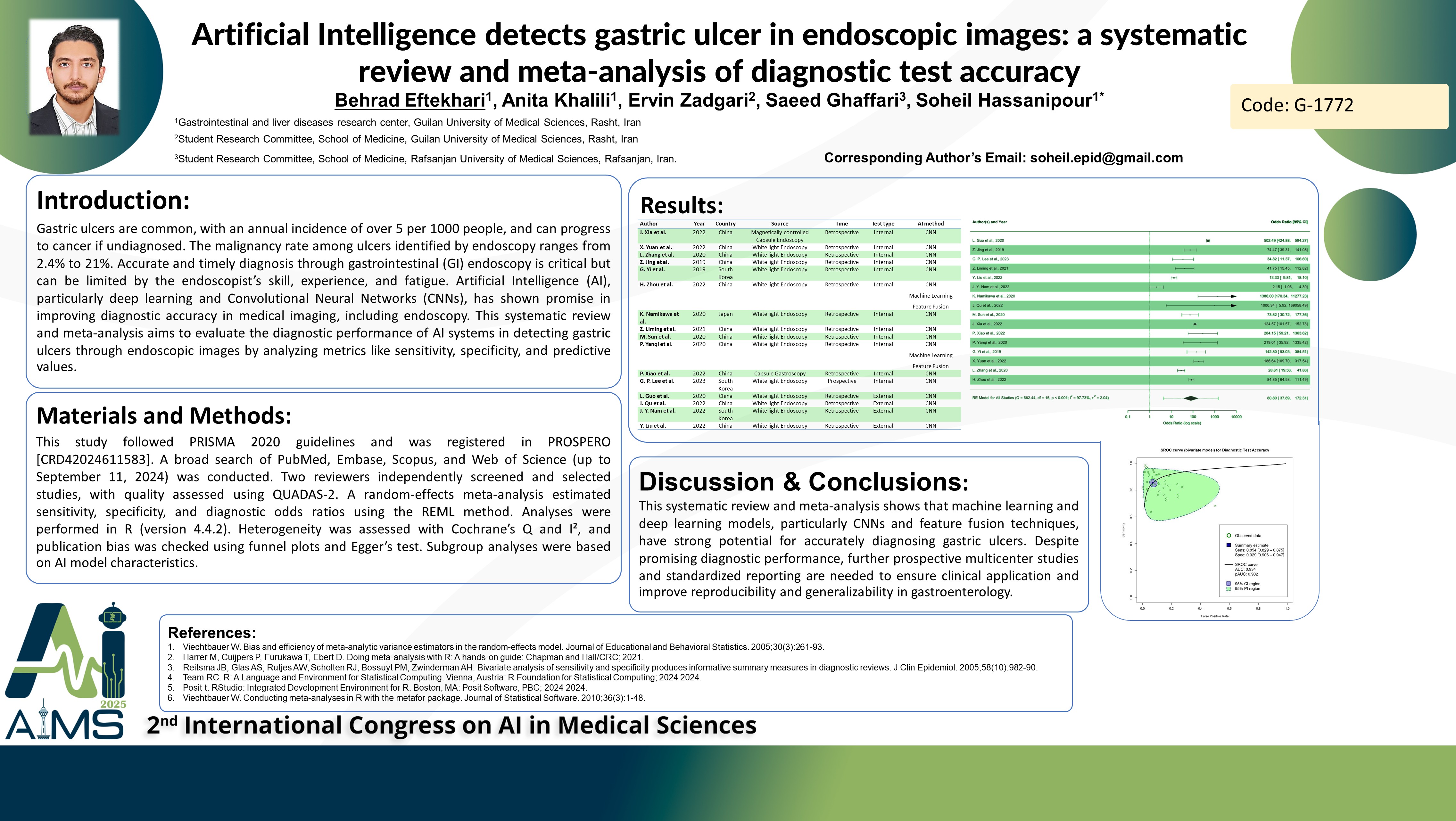
Background and Objective: Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) affects 5-10% of the global population and can lead to gastric cancer if not detected early. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology may improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, but there is insufficient evidence on its specific performance for diagnosing gastric ulcers. This study aims to evaluate image-based machine learning and deep learning techniques for diagnosing gastric ulcers, with the goal of guiding clinical decision-making and future research. Search Method: We performed a systematic search in PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science until September 11, 2024. QUADAS-2 was selected to judge the risk of bias in the included articles. Independent reviewers screened studies and assessed eligibility, certainty of evidence, and risk of bias. A univariate meta-analysis was conducted to calculate the sensitivity, specificity, and, subsequently, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), and negative likelihood ratio (LR-), along with the bivariate Reitsma method to compute SROC using R version 4.4.2. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database [CRD42024611583]. Findings: Twenty-three studies were eligible for qualitative analysis, of which sixteen were included in quantitative meta-analysis. The pooled DOR, sensitivity, and specificity of classification of gastric ulcer against other lesions or normal tissue were 80.80 [95% CI: 37.89 – 172.31], 0.854 [95% CI: 0.829 – 0.875], and 0.929 [95% CI: 0.906 – 0.947], respectively. The studies analyzing only CNN showed a DOR of 76.78 [95% CI: 32.53 – 181.22], while studies utilizing machine learning and feature fusion, in addition to the convolutional neural network, exhibited a DOR of 87.93 [95% CI: 61.74 – 125.23]. The SROC curve analysis reveals a diagnostic test with a high AUC of 0.934 [95% CI], indicating excellent overall accuracy and reliability for clinical application. Conclusion: Machine learning and Deep learning models demonstrate promising potential in detecting gastric ulcers in classification tasks against other pathologies. Further prospective multicenter studies, with standardized reporting of algorithms and modality parameters, are needed to validate these findings.
کلمات کلیدی
Gastric Ulcer, Endoscopy, Artificial Intelligence