تحلیل درونرایانهای بیان ژن و شبکههای پروتئینی در سلولهای بنیادی پرتوان القایی (iPSCs) و کاردیومیوسیتهای مشتقشده از سلولهای بنیادی پرتوان القایی برای پیشبرد پزشکی بازساختی و مهندسی بافت
کد: G-1764
نویسندگان: Melika Emarati ℗, Hossein Azizi *, Nima Ghasemi
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: آنالیز دادگان اومیکس
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
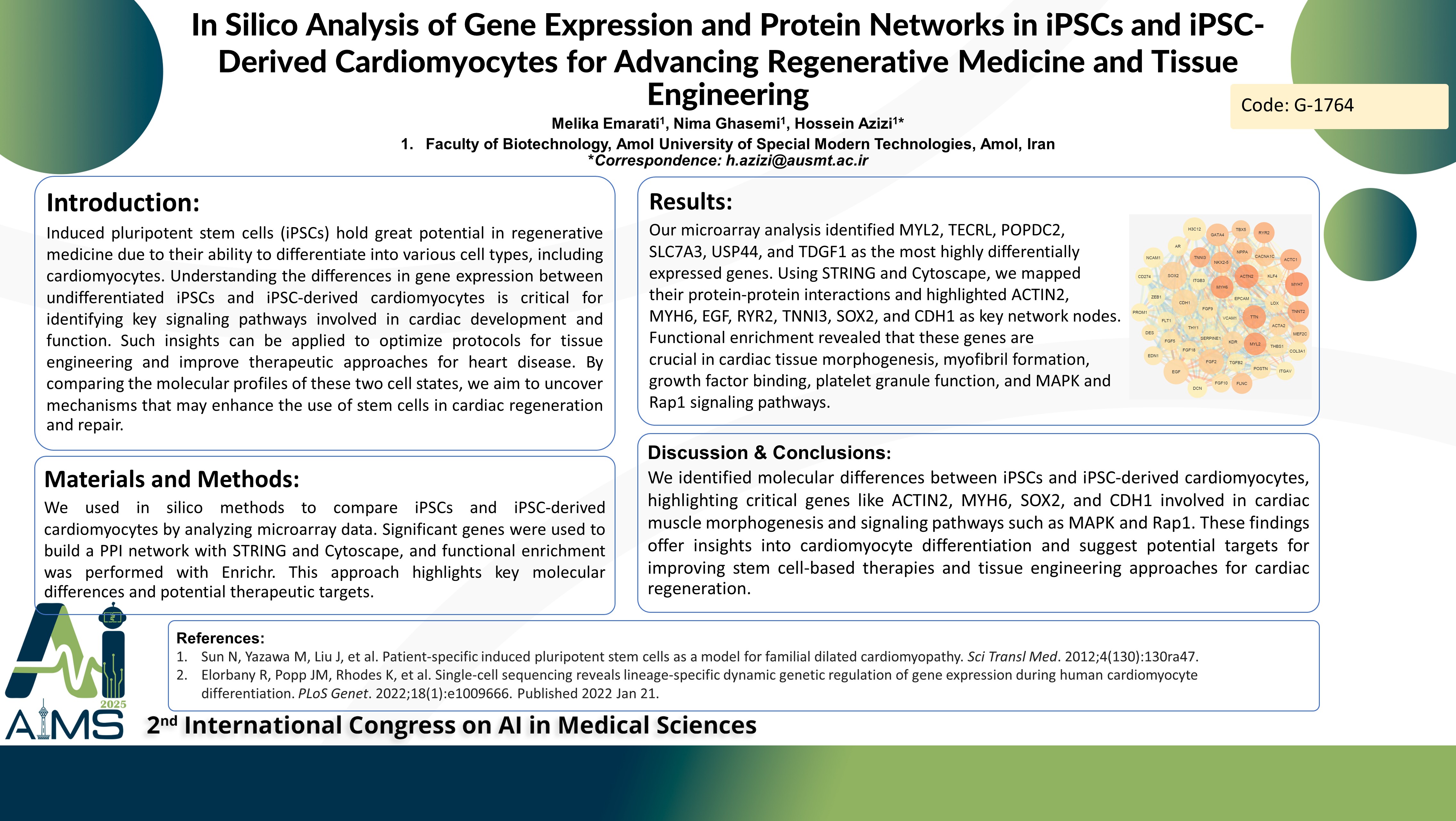
Background: Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have potential in regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cardiomyocytes. Understanding the differences in gene expression between undifferentiated iPSCs and iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes is critical for identifying key signaling pathways involved in cardiac development and function. Such insights can be applied to optimize protocols for tissue engineering and improve therapeutic approaches for heart disease. By comparing the molecular profiles of these two cell states, we aim to uncover mechanisms that may enhance the use of stem cells in cardiac regeneration and repair. Methods: We employed in silico methods to compare iPSCs with iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Microarray datasets from the GEO repository were analyzed through the GEO2R tool. Significantly differentially expressed genes were used to construct and analyze a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network utilizing the STRING and Cytoscape tools. Functional enrichment analysis was performed using the Enrichr platform to investigate the roles of key clusters. This approach, which identifies crucial nodes in the PPI network, offers valuable insights into the molecular distinctions between iPSCs and iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, opening new avenues for therapeutic development. Result: Our microarray analysis revealed that MYL2, TECRL, POPDC2, SLC7A3, USP44, and TDGF1 exhibited the highest fold changes among the differentially expressed genes. To visualize the protein-protein interactions of these DEGs, we employed the STRING database to construct a comprehensive interaction network. Using Cytoscape, we identified key genes driving the differentiation of iPSCs into cardiomyocytes. Notably, ACTIN2, MYH6, EGF, RYR2, TNNI3, SOX2, and CDH1 emerged as the most critical nodes in the network. Further functional enrichment analysis predicted that these central DEGs play pivotal roles in processes such as ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis, myofibril formation, fibroblast growth factor receptor binding, platelet alpha granule function, as well as involvement in the MAPK and Rap1 signaling pathways. Conclusion: We identified molecular differences between iPSCs and iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, highlighting critical genes like ACTIN2, MYH6, SOX2, and CDH1 involved in cardiac muscle morphogenesis and signaling pathways such as MAPK and Rap1. These findings offer insights into cardiomyocyte differentiation and suggest potential targets for improvement.
کلمات کلیدی
iPSCs, Cardiomyocytes, Gene Expression, Protein-Interaction