استفاده از هوش مصنوعی در قالب سیستم تصمیم یار بالینی در مدیریت درمان دارویی سرطان
کد: G-1064
نویسندگان: Tayeb Ramim * ℗
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: سیستم های تصمیم یار بالینی
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
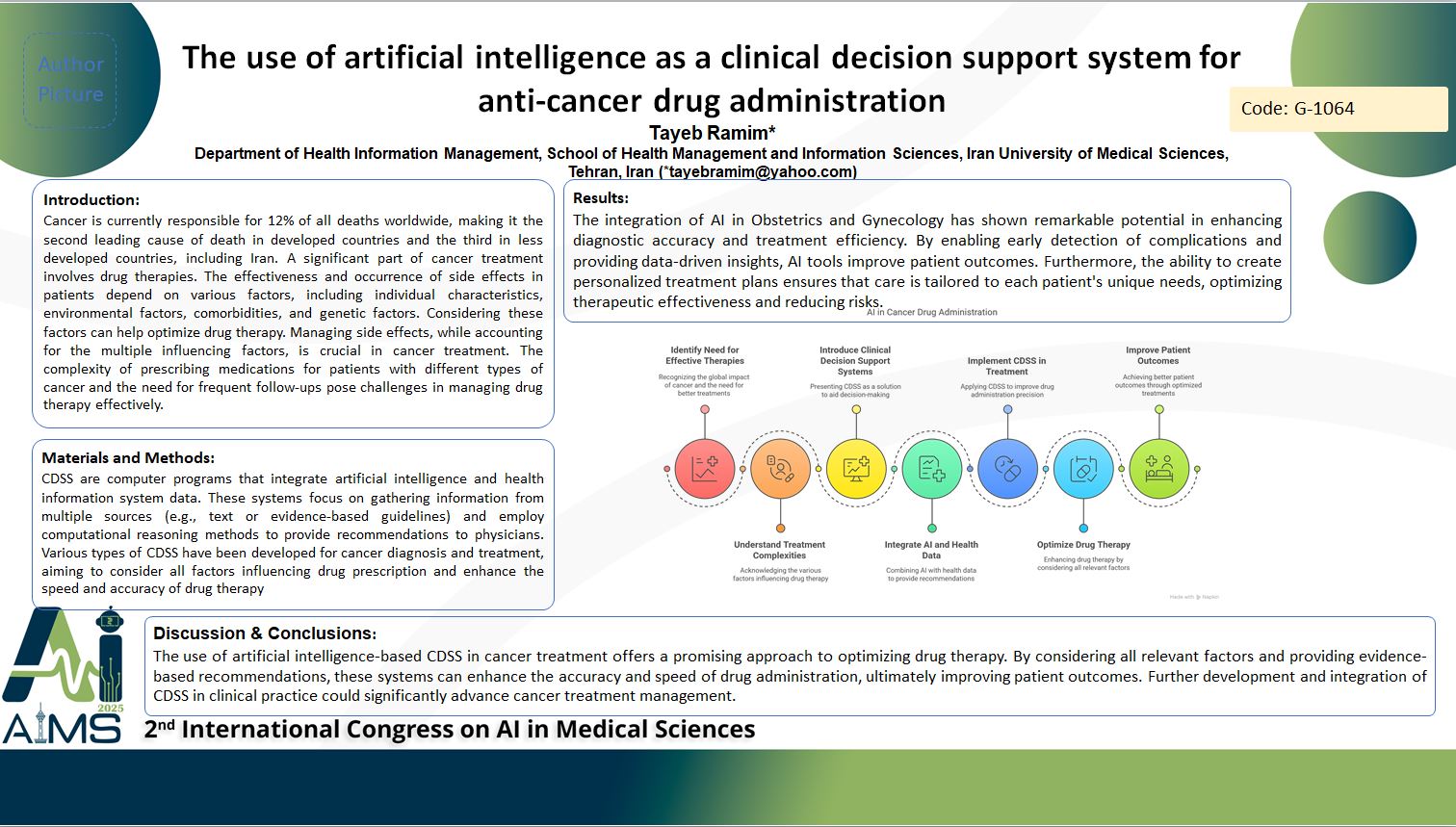
Background and aims: Cancer is currently responsible for 12% of all deaths worldwide, making it the second leading cause of death in developed countries and the third in less developed countries, including Iran. A significant part of cancer treatment involves drug therapies. The effectiveness and occurrence of side effects in patients depend on various factors, including individual characteristics, environmental factors, comorbidities, and genetic factors. Considering these factors can help optimize drug therapy. Managing side effects, while accounting for the multiple influencing factors, is crucial in cancer treatment. The complexity of prescribing medications for patients with different types of cancer and the need for frequent follow-ups pose challenges in managing drug therapy effectively. The use of advanced technologies, such as Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS), can assist physicians in this process. CDSS are designed to aid physicians in decision-making tasks, utilizing artificial intelligence and health information system data to provide recommendations based on evidence-based guidelines and computational reasoning. Method: CDSS are computer programs that integrate artificial intelligence and health information system data. These systems focus on gathering information from multiple sources (e.g., text or evidence-based guidelines) and employ computational reasoning methods to provide recommendations to physicians. Various types of CDSS have been developed for cancer diagnosis and treatment, aiming to consider all factors influencing drug prescription and enhance the speed and accuracy of drug therapy. Results: The implementation of CDSS in cancer treatment has shown potential in improving the precision and efficiency of drug administration. By integrating multiple factors such as patient-specific data, environmental influences, and genetic information, these systems can optimize drug therapy and reduce adverse effects. Additionally, CDSS can streamline the decision-making process for physicians, enabling more personalized and effective treatment plans. Conclusion: The use of artificial intelligence-based CDSS in cancer treatment offers a promising approach to optimizing drug therapy. By considering all relevant factors and providing evidence-based recommendations, these systems can enhance the accuracy and speed of drug administration, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Further development and integration of CDSS in clinical practice could significantly advance cancer treatment management.
کلمات کلیدی
Artificial Intelligence, Clinical Decision Support Systems