Advances in artificial intelligence, robotics, augmented and virtual reality in neurosurgery
Code: G-1640
Authors: Kimia Kazemzadeh * ℗, Meisam Akhlaghdoust, Alireza Zali
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Robotics in Surgery and Care
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
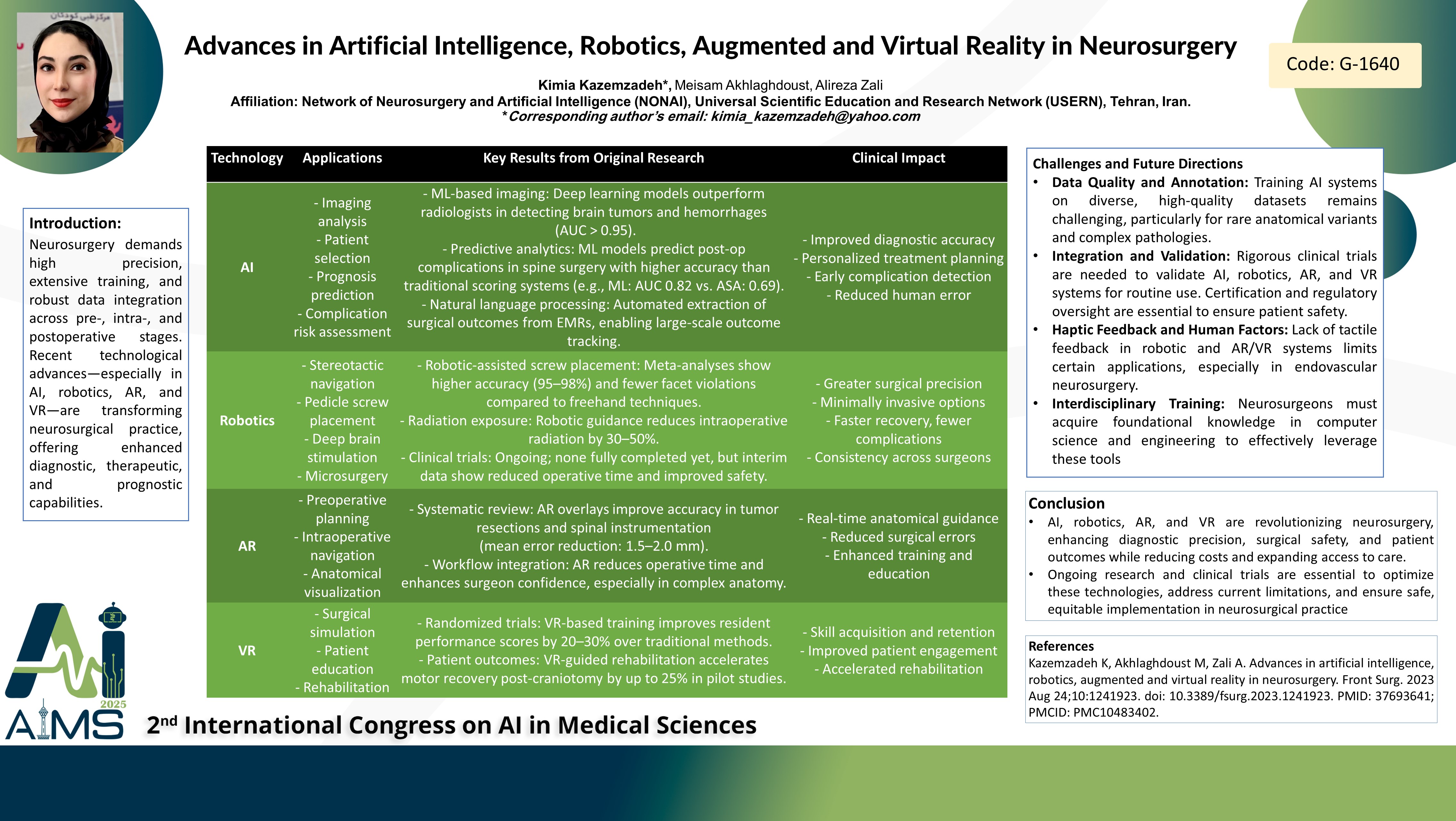
Abstract
Background and Aim: Neurosurgery is a complex field requiring extensive training and precise data acquisition throughout pre-, intra-, and postoperative phases. Over the past decade, artificial intelligence (AI) has become increasingly significant in neurosurgery, enhancing diagnostic and prognostic outcomes. This review aims to explore the roles of AI, robotics, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) in neurosurgery, focusing on their potential to improve patient care and reduce healthcare costs. Method: This narrative review integrates findings from various articles to elucidate the applications of AI, robotics, AR, and VR in neurosurgery. The review covers preoperative planning, intraoperative decision-making, and postoperative care, highlighting how these technologies enhance surgical precision, reduce errors, and facilitate data management. Result: AI algorithms have been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing large datasets, including imaging and clinical records. AI-assisted tools aid neurosurgeons in making informed decisions during surgical interventions, enhancing patient outcomes. Additionally, AI helps in predicting patient recovery trajectories and potential complications, allowing for more personalized postoperative care. Robotic systems provide enhanced precision and dexterity, reducing the risk of complications during complex neurosurgical procedures. Robotics also facilitate minimally invasive surgeries, leading to faster recovery times and reduced hospital stays. AR and VR technologies are instrumental in preoperative planning, allowing neurosurgeons to visualize complex anatomical structures and simulate surgical procedures. Intraoperatively, AR enhances visualization by overlaying critical anatomical information onto the surgical site, improving surgical precision. VR is used in patient education and rehabilitation, enhancing patient engagement and recovery. The use of these technologies can lead to cost savings by reducing the length of hospital stays and minimizing the need for repeat surgeries. Furthermore, they enable the delivery of high-quality healthcare to a broader population by enhancing surgical efficiency and accessibility. Conclusion: The incorporation of AI, robotics, AR, and VR in neurosurgery represents a significant advancement in the field, offering improved patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery. As these technologies continue to evolve, they are poised to play an increasingly vital role in enhancing neurosurgical practices and patient care.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, Neurosurgery, Robotics