A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining Algorithms for Early Lung Cancer Detection: A Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Networks ,Classification , and Optimization Techniques
Code: G-1626
Authors: Nahid Askari *, Sama Samadzadegan ℗
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
Abstract
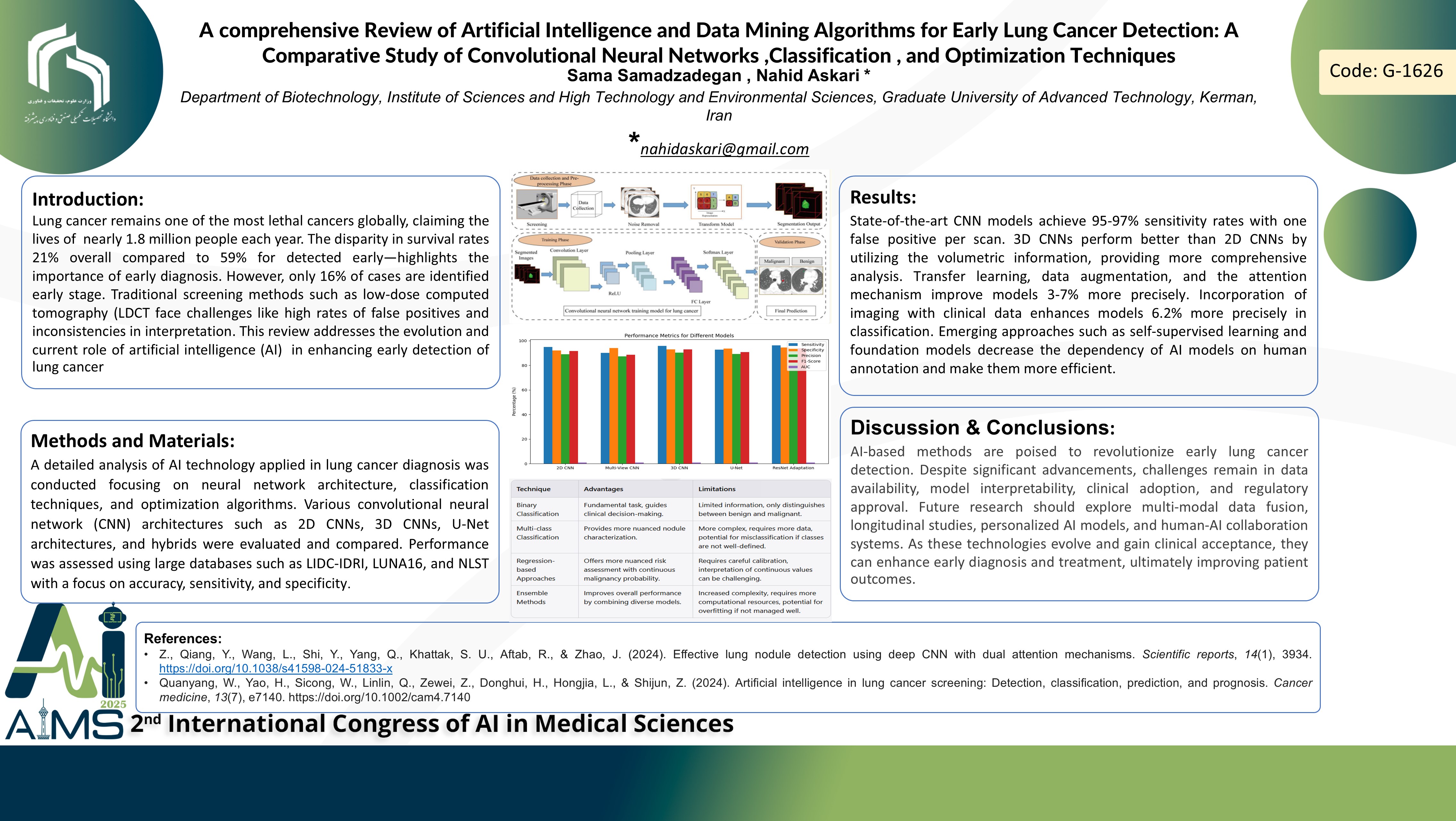
Background and aims: Lung cancer remains one of the most lethal cancers globally, claiming the lives of nearly 1.8 million people each year. The disparity in survival rates 21% overall compared to 59% for detected early—highlights the importance of early diagnosis. However, only 16% of cases are identified early stage. Traditional screening methods such as low-dose computed tomography (LDCT face challenges like high rates of false positives and inconsistencies in interpretation. This review addresses the evolution and current role of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing early detection of lung cancer. Method: A detailed analysis of AI technology applied in lung cancer diagnosis was conducted focusing on neural network architecture, classification techniques, and optimization algorithms. Various convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures such as 2D CNNs, 3D CNNs, U-Net architectures, and hybrids were evaluated and compared. Performance was assessed using large databases such as LIDC-IDRI, LUNA16, and NLST with a focus on accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. Result: State-of-the-art CNN models achieve 95-97% sensitivity rates with one false positive per scan. 3D CNNs perform better than 2D CNNs by utilizing the volumetric information, providing more comprehensive analysis. Transfer learning, data augmentation, and the attention mechanism improve models 3-7% more precisely. Incorporation of imaging with clinical data enhances models 6.2% more precisely in classification. Emerging approaches such as self-supervised learning and foundation models decrease the dependency of AI models on human annotation and make them more efficient. Conclusion: AI-based methods are on the verge of revolutionizing early lung cancer detection. The advancements are staggering, but challenges remain in areas such as data availability, model interpretability, clinical adoption, and regulatory clearance. Data fusion across multiple modalities, longitudinal cohorts, personalized AI models, and human-AI team systems are some of the directions that need to be explored in the future. As they these technologies continue to develop and gain clinical acceptance, these technologies can make a significant impact by enhancing early diagnosis and treatment, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, lung Cancer, CNN,Early Detection