پیش بینی درجه حرکت انگشتان دست بر اساس سیگنالهای مغزی الکتروکورتیکوگرافی مبتنی بر شبکه عصبی CNN و LSTM و مکانیزم توجه
کد: G-1620
نویسندگان: Yekta Rasoulzadeh * ℗, سیده زهره سیدصالحی
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: پردازش سیگنال های پزشکی
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
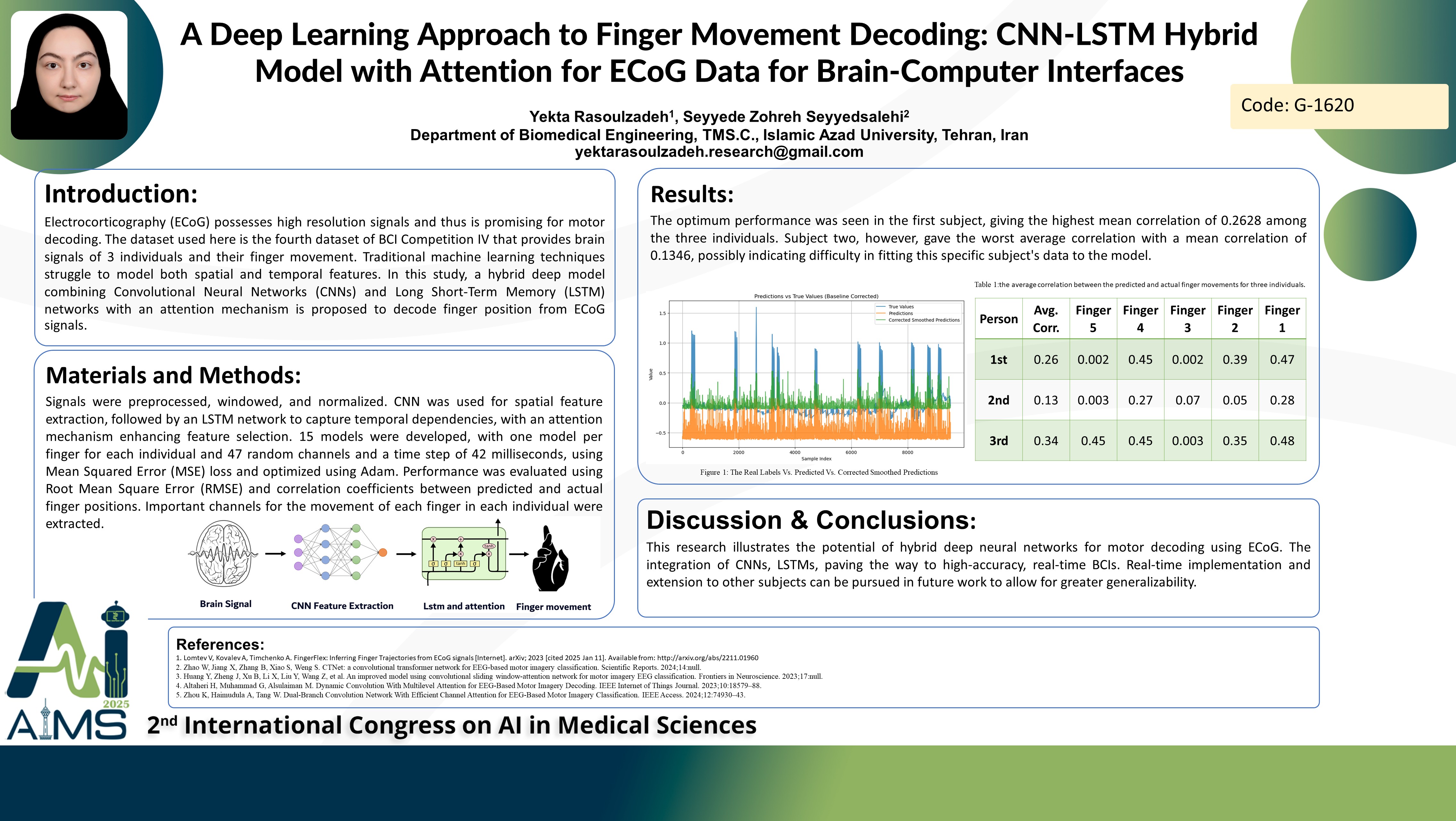
Background and aims: Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) interpret brain activity to control external devices, virtual speech recognition, and assist individuals with motor disorders. Electrocorticography (ECoG) possesses high resolution signals and thus is promising for motor decoding. The dataset used here is the fourth dataset of BCI Competition IV that provides brain signals of 3 individuals and their finger movement. Traditional machine learning techniques struggle to model both spatial and temporal features. In this study, a hybrid deep model combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks with an attention mechanism is proposed to decode finger position from ECoG signals. Method: Signals were preprocessed, windowed, and normalized. CNN was used for spatial feature extraction, followed by an LSTM network to capture temporal dependencies, with an attention mechanism enhancing feature selection. 15 models were developed, with one model per finger for each individual and 47 random channels and a time step of 42 milliseconds, using Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss and optimized using Adam. Performance was evaluated using Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and correlation coefficients between predicted and actual finger positions. Important channels for the movement of each finger in each individual were extracted. Results: The optimum performance was seen in the first subject, giving the highest mean correlation of 0.2628 among the three individuals. Subject two, however, gave the worst average correlation with a mean correlation of 0.1346, possibly indicating difficulty in fitting this specific subject's data to the model. Fingers 1, 2, and 4 consistently had higher average correlation coefficients, especially for subjects 1 and 3. Finger 3 showed very poor performance (values close to zero for all subjects). Moreover, model comparison shows that the finger-ECoG channel correlation varies across subjects. Some fingers with better model performance are highly correlated with specific channels. Conclusion: This paper illustrates the potential of hybrid deep neural networks for motor decoding using ECoG. The integration of CNNs, LSTMs, paving the way to high-accuracy, real-time BCIs. Real-time implementation and extension to other subjects can be pursued in future work to allow for greater generalizability.
کلمات کلیدی
ECoG, CNN, LSTM, attention, Finger Movement