Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Driven Biomarker Analysis on Survival Outcomes in Lung Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review
Code: G-1590
Authors: Mohammad Bastani ℗, Mohammad Alizadeh, Aynaz Esmailzadeh, Nahid Mehrabi *, Mahdi Ghorbani
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
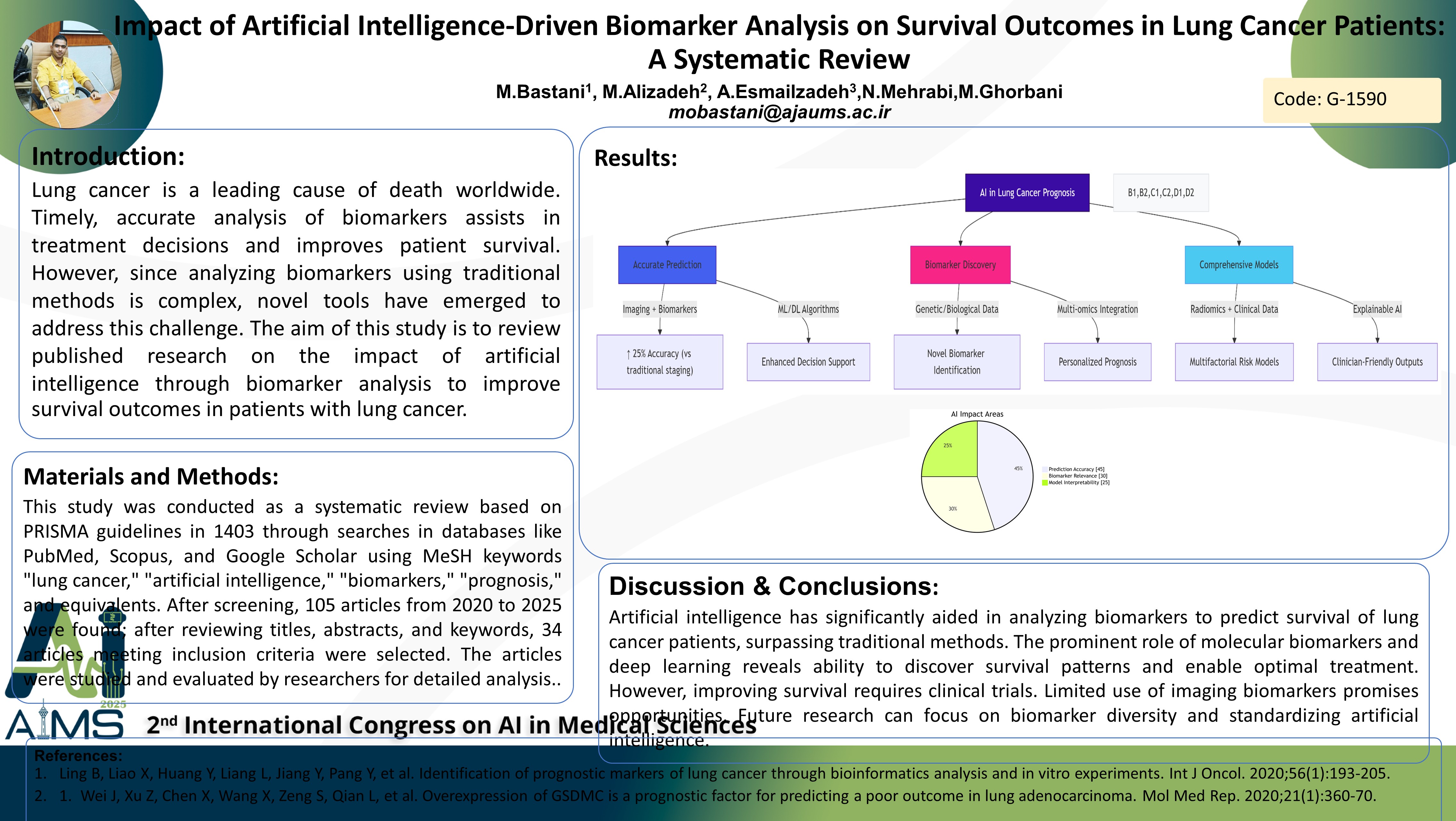
Abstract
Background and aims: Lung cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide. Timely, accurate analysis of biomarkers assists in treatment decisions and improves patient survival. However, since analyzing biomarkers using traditional methods is complex, novel tools have emerged to address this challenge. The aim of this study is to review published research on the impact of artificial intelligence through biomarker analysis to improve survival outcomes in patients with lung cancer. Method: This study was conducted as a systematic review based on PRISMA guidelines in 1403 through searches in databases like PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar using MeSH keywords "lung cancer," "artificial intelligence," "biomarkers," "prognosis," and equivalents. After screening, 105 articles from 2020 to 2025 were found; after reviewing titles, abstracts, and keywords, 34 articles meeting inclusion criteria were selected. The articles were studied and evaluated by researchers for detailed analysis. Results: The research findings showed that artificial intelligence in lung cancer prognosis falls mainly into these three categories: 1) Accurate prognosis prediction, in which artificial intelligence models are designed to predict lung cancer prognosis based on imaging data and biomarkers with a higher degree of accuracy. This also includes effectively applying machine learning and deep learning to enhance medical decision support systems. 2) Identification of effective biomarkers, where these applications incorporate biological and genetic data to improve the efficacy of prognosis prediction and marker identification in lung cancer. 3) Building comprehensive prognostic models, where these applications integrate image data with biomarkers and clinical data to build multifactorial models for predicting lung cancer prognosis together with serving the physician in clinical decisions. Conclusion: Artificial intelligence has significantly aided in analyzing biomarkers to predict survival of lung cancer patients, surpassing traditional methods. The prominent role of molecular biomarkers and deep learning reveals ability to discover survival patterns and enable optimal treatment. However, improving survival requires clinical trials. Limited use of imaging biomarkers promises opportunities. Future research can focus on biomarker diversity and standardizing artificial intelligence.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, Biomarkers, Lung-cancer, Survival