تحلیل تطبیقی پاسخ های چت جی پی تی و صاحب حیوان خانگی غیرمعمول با توجه به دانش، نگرش، و عملکرد در رابطه با بیماری های انگلی زئونوز
کد: G-1584
نویسندگان: Fatemeh Haji Agha Khiyabani * ℗, Negar Najafi Fard, Fateme Jalousian
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: دستیار مجازی هوشمند
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
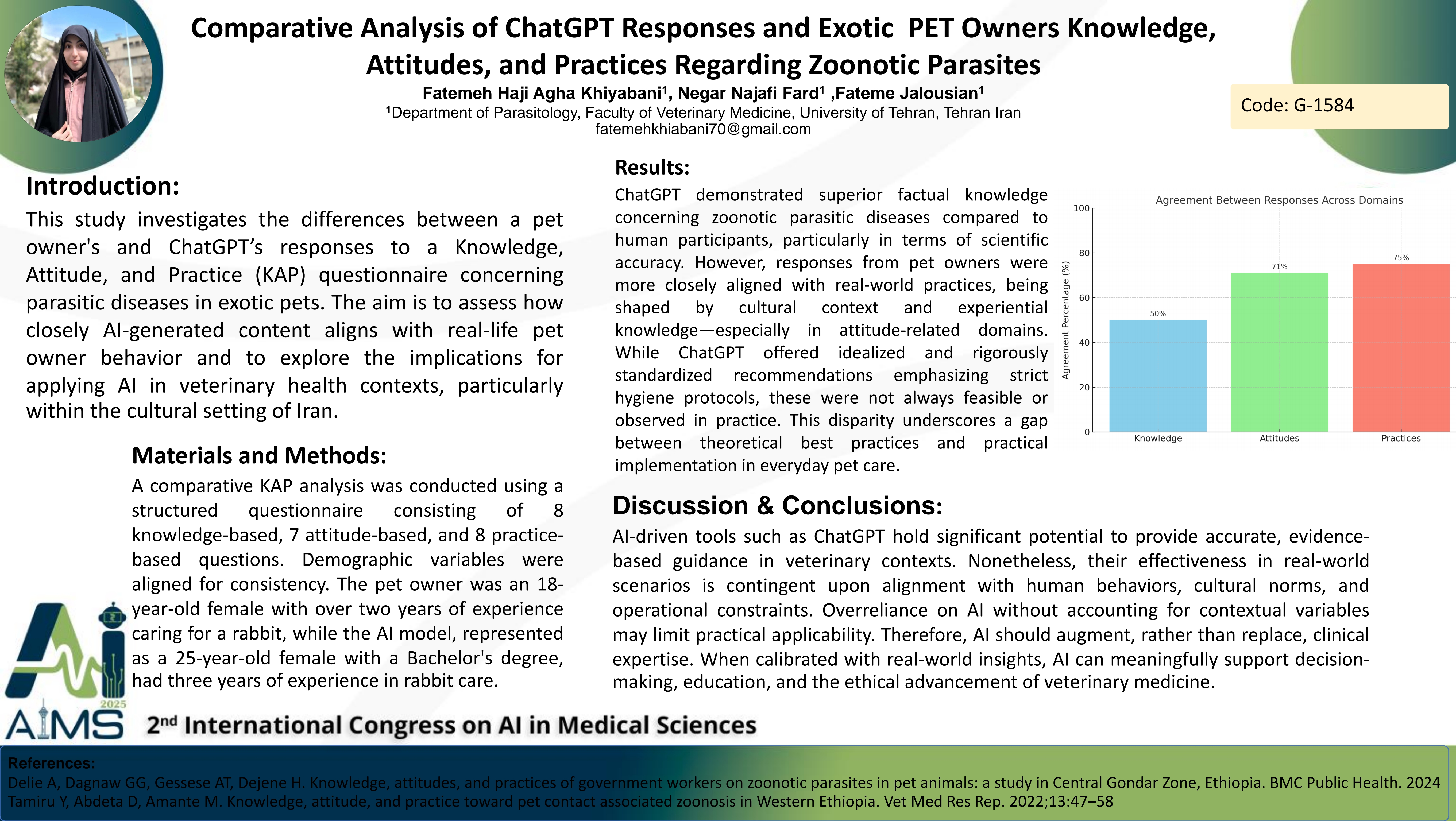
Background and Aims: This study investigates the differences between a pet owner's and ChatGPT’s responses to a Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice (KAP) questionnaire concerning parasitic diseases in exotic pets. The aim is to assess how closely AI-generated content aligns with real-life pet owner behavior and to explore the implications for applying AI in veterinary health contexts, particularly within the cultural setting of Iran. Method: A comparative KAP analysis was conducted using a structured questionnaire consisting of 8 knowledge-based, 7 attitude-based, and 8 practice-based questions. Demographic variables were aligned for consistency. The pet owner was an 18-year-old female with over two years of experience caring for a rabbit, while the AI model, represented as a 25-year-old female with a Bachelor's degree, had three years of experience in rabbit care. Result: Agreement between responses varied across domains: knowledge (50%), attitudes (71%), and practices (75%). ChatGPT exhibited broader factual knowledge about zoonotic parasitic diseases, outperforming the human participant in scientific accuracy. However, in attitude-related responses, the pet owner's answers were more culturally grounded and reflective of real-life experiences, thus appearing more applicable in a local context. For attitude-related responses, pet owners’ answers appeared more acceptable, as they aligned more closely with cultural and practical aspects of pet ownership. Their responses reflected real-life experiences and social norms, making them more relevant to actual pet care practices. ChatGPT provided idealized and highly standardized recommendations for pet care, emphasizing strict hygiene and health measures. However, in reality, pet owners did not always adhere to these high standards, demonstrating a gap between theoretical best practices and real-world implementation. Conclusion: AI tools like ChatGPT can offer accurate, evidence-based guidance, but their real-world effectiveness depends on contextual alignment with human behavior and constraints. AI-generated outputs often overlook cultural norms, experiential knowledge, and logistical realities. Thus, interpretation through a human lens remains essential. For effective integration into veterinary practice, AI must support rather than replace clinical judgment. When calibrated with real-world feedback, AI can enhance veterinary decision-making, education, and communication, contributing meaningfully and ethically to the advancement of veterinary science.
کلمات کلیدی
AI, Veterinary, Zoonosis, KAP Study, Parasitic