An Evolution in Breast Cancer Prediction: a Systematic Review on the Role of the Artificial Intelligence
Code: G-1581
Authors: Reza Sadghifar * ℗, Fereshteh Pirani, Motahareh Ebrahimi
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
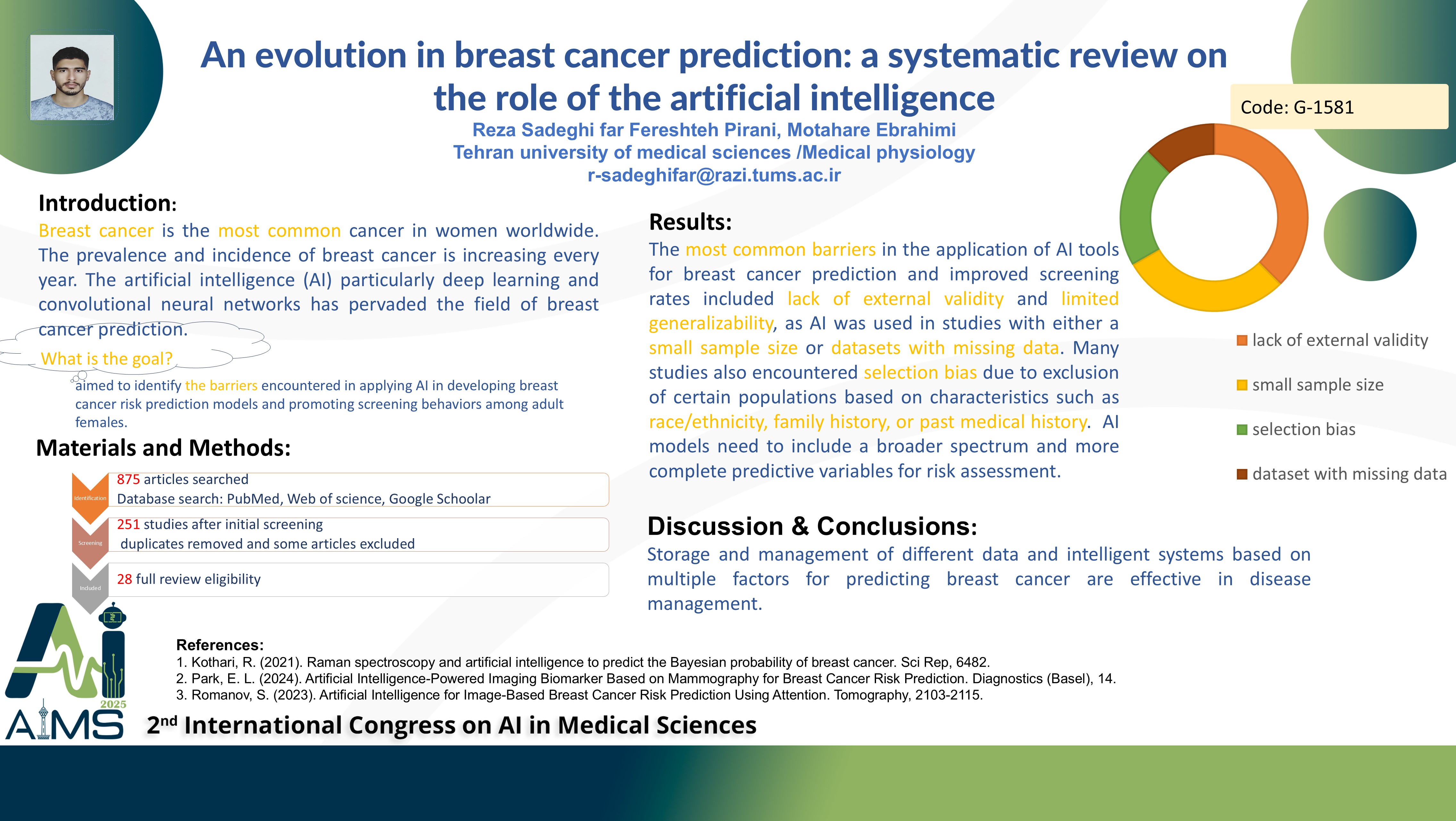
Abstract
Background and Aims: Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide. The prevalence and incidence of breast cancer is increasing every year. The artificial intelligence (AI) particularly deep learning and convolutional neural networks has pervaded the field of breast cancer prediction. This systematic review aimed to identify the barriers encountered in applying AI in developing breast cancer risk prediction models and promoting screening behaviors among adult females. Methods: This review was performed independently based on PICO criteria and PRISMA checklist, a total number of 251 studies between 2020 and 2025 were obtained from these databases: PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. We applied inclusion and exclusion criteria to the search; 28 studies were identified. Result: The most common barriers in the application of AI tools for breast cancer prediction and improved screening rates included lack of external validity and limited generalizability, as AI was used in studies with either a small sample size or datasets with missing data. Many studies also encountered selection bias due to exclusion of certain populations based on characteristics such as race/ethnicity, family history, or past medical history. AI models need to include a broader spectrum and more complete predictive variables for risk assessment. Investigating long-term outcomes with improved follow-up periods is critical to assess the impacts of AI on clinical decisions beyond just the immediate outcomes. Conclusion: Storage and management of different data and intelligent systems based on multiple factors for predicting breast cancer are effective in disease management.
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence, Breast Cancer, Predict