بازکاربردیابی آنالوگ های آسیمینیب و داروهای مورد تایید FDA در رده های سلولی لوسمی میلوئیدی مزمن مبتنی بر روش های یادگیری ماشین
کد: G-1549
نویسندگان: Reza Mohammad Zade Makuee ℗, Nima Razzaghi-Asl *, Amin Ashna Moghadam
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: کشف و طراحی دارو
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
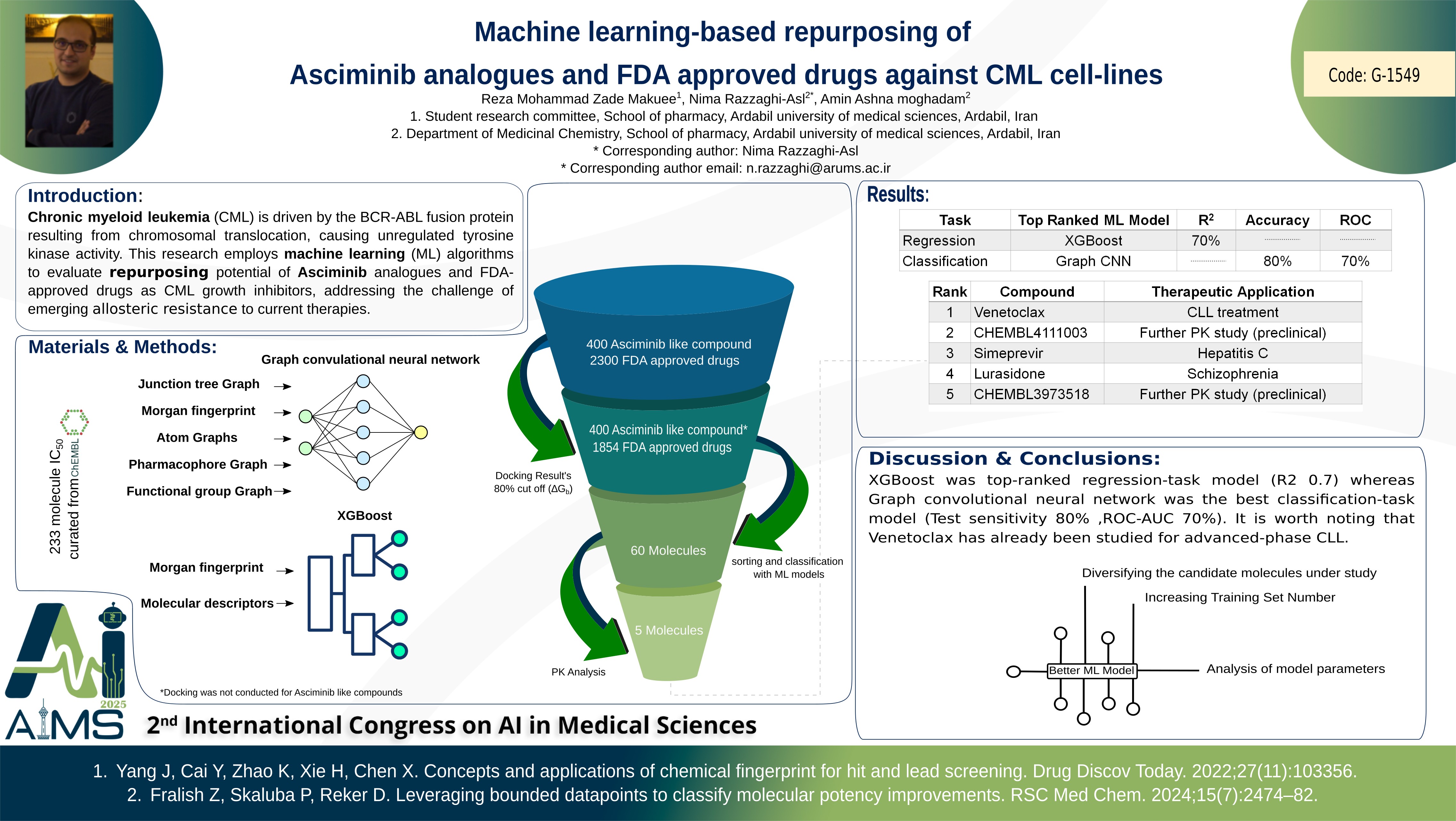
Background and aims: Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a type of blood cancer driven by BCR-ABL fusion protein. This abnormal protein results from chromosomal translocation leading to unregulated tyrosine kinase (TK) activity. Despite satisfying clinical outcomes, Asciminib, a later-generation TK inhibitor, faces challenges due to emerging allosteric resistance. This issue necessitates the query for alternative compounds. Within present contribution, various machine learning (ML) algorithms were utilized to evaluate the repurposing potential of Asciminib analogues and FDA approved drugs as growth inhibitors of CML-related cancerous cell lines. Method: A dataset comprising 233 small molecules with relevant cell-based(K562,BV173) IC50 values was curated from ChEMBL database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/). Morgan fingerprint, atom graphs, pharmacophore Graph (one-hot-encoded pharmacophore as node, bonds type as edge), junction tree graph (generated by converting bonds, rings and junction atoms to nodes) and functional group graph (predefined groups as nodes, and predefined bond as edge) were calculated for each molecule under study as a feature. AutoDock-GPU was used to calculate mean-binding free energies for each molecule in the allosteric site of wild and mutant BCR-ABL. We designed a graph convolutional neural network to learn from paired data and choose active one subsequently. Other promising ML algorithms such as XGBoost and Random Forest were also tested. Subsequently, the trained models were used to predict the repurposing potential of Asciminib like molecules and FDA drugs. Results: XGBoost was top-ranked regression-task model (R2 = 0.7) whereas Graph convolutional neural network was the best classification-task model (80% for test sensitivity and 70% for ROC-AUC value). Top-ranked Asciminib like molecules and FDA drugs were found to be Venetoclax, CHEMBL4111003, Simeprevir, Lurasidone and CHEMBL3973518. It is worth noting that Venetoclax has already been studied for advanced-phase CML. Moreover, CHEMBL4111003 and CHEMBL3973518 were subjected to in-silico pharmacokinetics analysis in terms of bioavailability and metabolism. Conclusion: Overall ML models showed promising results only when fed with proper data and subsequently hypertuned. On the basis of outlined computational workflow, diversifying the candidate molecules under study could suggest more potent and mutation-resistant CML candidates. Further analysis of model parameters within larger train sets is under investigation.
کلمات کلیدی
BCR-ABL, Drug Repurposing, Machine learning