نقش هوش مصنوعی (AI) در پیشبرد تحویل داروهای سرطان و پزشکی ترمیمی: نوآوریها و چالشها
کد: G-1512
نویسندگان: Parinaz Nezhad-Mokhtari * ℗, MirAhmad Mazloomi, Sara Almasi Nezhad
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: تشخیص و درمان سرطان
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
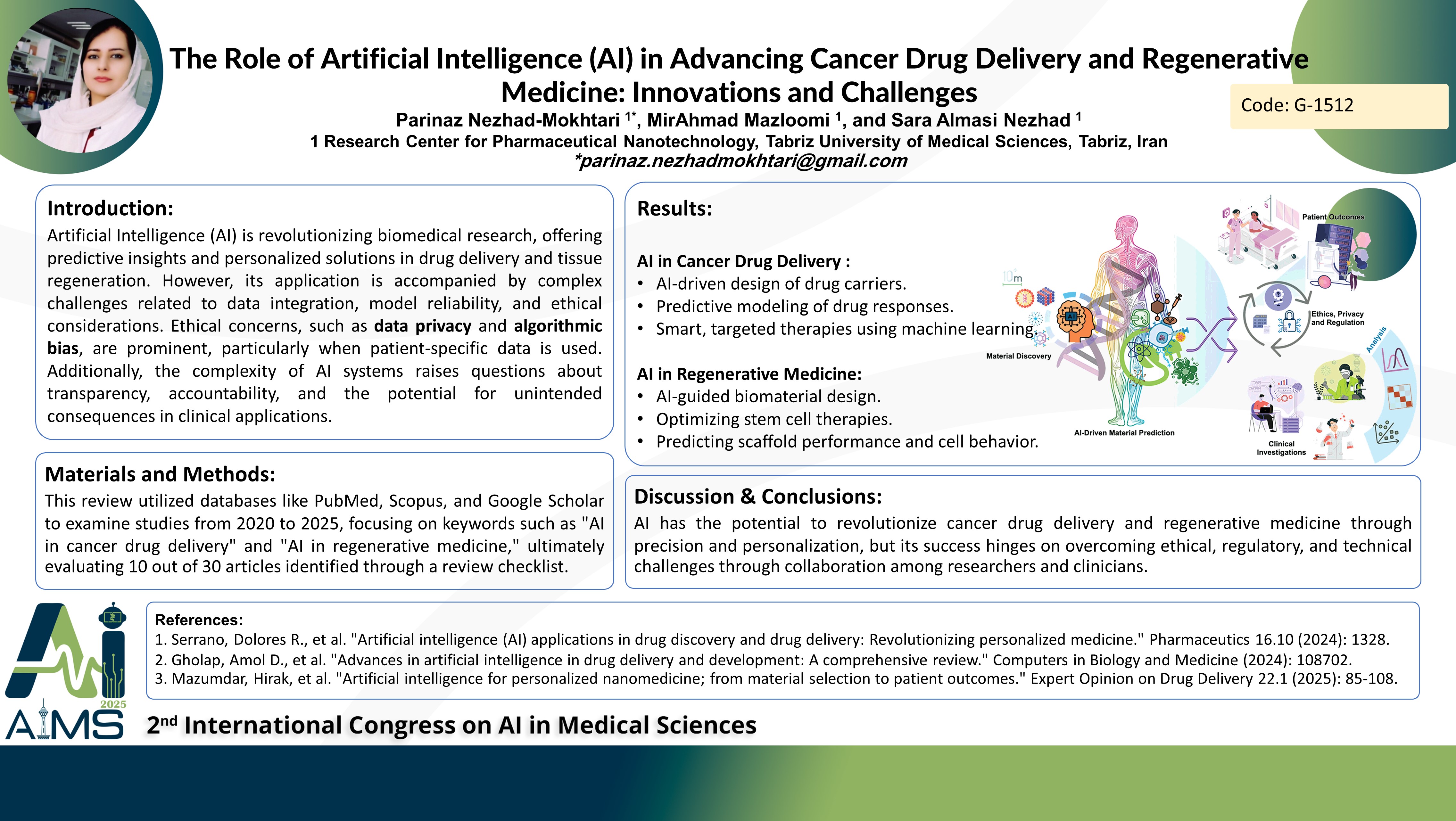
Background and aims: Artificial Intelligence (AI) employs advanced algorithms and computational models to replicate human cognitive functions such as learning, pattern recognition, and decision-making. In cancer drug delivery and regenerative medicine, AI is revolutionizing how therapies are developed, optimized, and administered. By leveraging large-scale data analysis, AI enables the design of targeted drug delivery systems and the development of personalized regenerative treatments, ultimately improving patient outcomes. This study examines the transformative potential of AI in these domains while also addressing the ethical and technical challenges associated with its implementation. Method: This systematic review was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases to identify relevant studies published between 2020 and 2025. Keywords included "AI in cancer drug delivery," "AI in regenerative medicine," "smart drug delivery systems," and "AI-driven tissue engineering." In the end, among the 60 articles obtained, 18 articles were evaluated with the checklist of review articles. Results: AI has significantly advanced drug delivery by enabling developing smart systems that can control the release of therapeutics exactly, optimize dosing, and target specific tissues or cells. Machine learning algorithms analyze pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data to predict drug behavior and improve formulation design. In regenerative medicine, AI facilitates the creation of biomaterials, scaffolds, and tissue engineering strategies tailored to individual patients. However, the integration of AI in these fields is not without challenges. Ethical concerns, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias, are prominent, particularly when patient-specific data is used. Additionally, the complexity of AI systems raises questions about transparency, accountability, and the potential for unintended consequences in clinical applications. Conclusion: AI is a powerful tool for advancing cancer drug delivery and regenerative medicine, offering unprecedented opportunities for precision and personalization. However, its successful implementation requires addressing ethical, regulatory, and technical challenges. Researchers and clinicians must collaborate to ensure that AI-driven innovations are safe, equitable, and effective. By overcoming these challenges, AI has the potential to transform healthcare, enabling more efficient drug delivery systems and groundbreaking regenerative therapies that improve patients' quality of life.
کلمات کلیدی
ArtificialIntelligence, CancerDrugDeliverySystems, RegenerativeMedicine, PersonalizedTherapies, MachineLearningAlgorithms