Creating a Spatial-based Map based on the Probability of Infection Visceral Leishmaniasis using Fuzzy Logic
Code: G-1315
Authors: Elahe Akbari * ℗
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Intelligent Virtual Assistant
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
Abstract
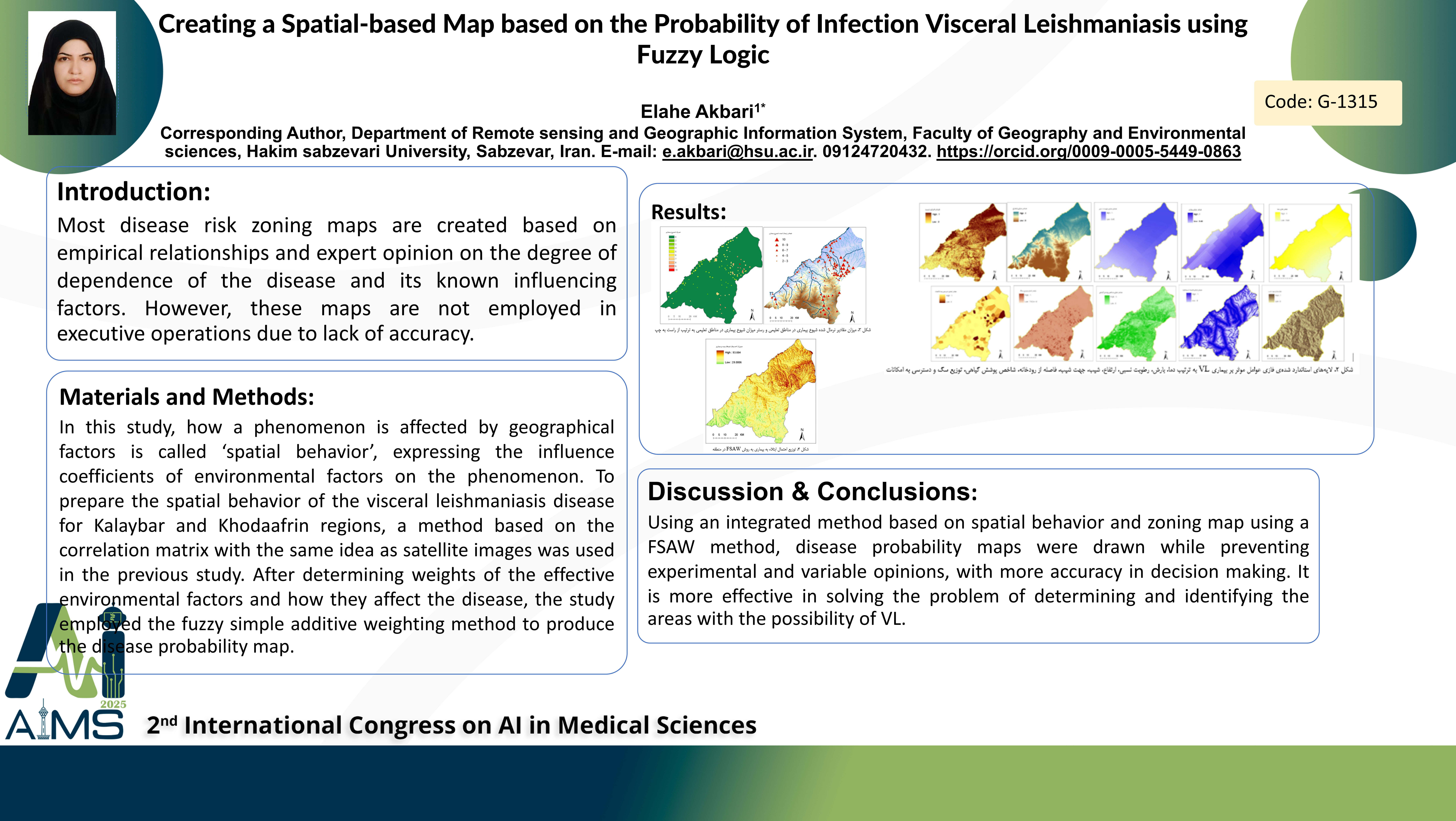
Background and aim: Most disease risk zoning maps are created based on empirical relationships and expert opinion on the degree of dependence of the disease and its known influencing factors. However, these maps are not employed in executive operations due to lack of accuracy. Methodology: In this study, how a phenomenon is affected by geographical factors is called ‘spatial behavior’, expressing the influence coefficients of environmental factors on the phenomenon. To prepare the spatial behavior of the visceral leishmaniasis disease for Kalaybar and Khodaafrin regions, a method based on the correlation matrix with the same idea as satellite images was used in the previous study. After determining weights of the effective environmental factors and how they affect the disease, the study employed the fuzzy simple additive weighting method to produce the disease probability map. Results: Comparing the infection probability map with the disease prevalence determined the FSAW method with the root mean squared error of 1.9389 individuals. Based on the probability map of disease, it was found that the DilBilmaz village and its surrounding settlements have the highest probability of the disease. Areas with higher heights (Qaradagh Mountains) located in the southwest of study area are considered to have lower disease prevalence. Conclusion: Using an integrated method based on spatial behavior and zoning map using a FSAW method, disease probability maps were drawn while preventing experimental and variable opinions, with more accuracy in decision making. It is more effective in solving the problem of determining and identifying the areas with the possibility of VL.
Keywords
Infection Map, Visceral Leishmaniasis, RS, GIS