پیش بینی پاسخ به تجویز کورتیکواستروئیدها در درمان بحران تنفسی کووید-19 مبتنی بر الگوریتم بیز
کد: G-1026
نویسندگان: Sarah Mousavi *, Seyed Ali Golestaneh ℗
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
برچسب: کشف و طراحی دارو
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
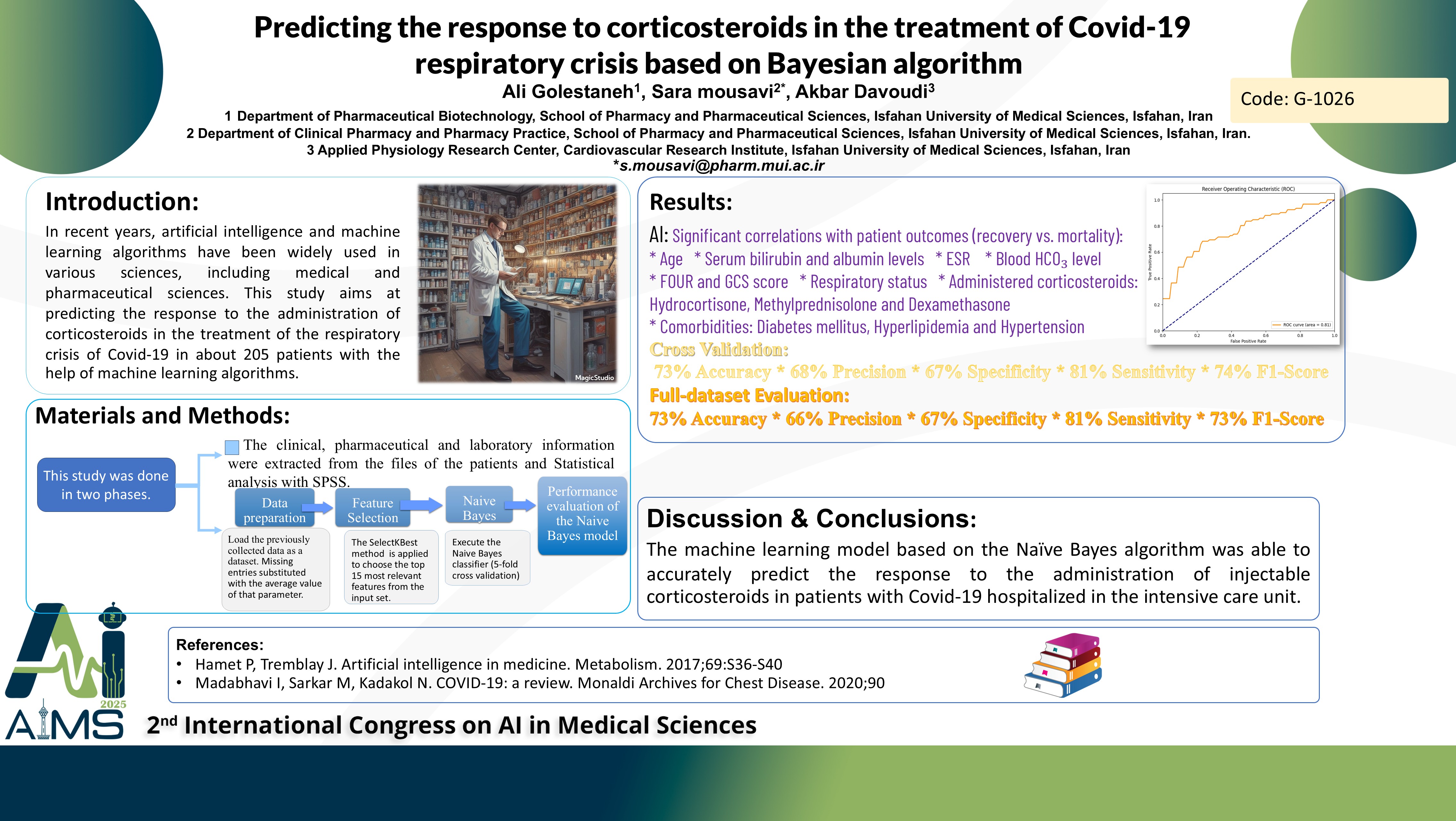
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have made significant advancements, particularly in the medical field, where they can enhance processes like drug development and diagnosis. This study focuses on using ML algorithms to predict responses to corticosteroid treatment in COVID-19 respiratory crises, aiming to provide insights into corticosteroid effectiveness. The study was conducted in two phases. Initially, data were gathered from medical records of 205 ICU patients at Al-Zahra Hospital between March and September 2021 who received corticosteroids, specifically dexamethasone. These patients had an average hospital stay of 23.1 days, with 16.1 days spent in the ICU. Key findings indicated that diabetes was the most prevalent condition among participants. Of the 205 patients, 92 recovered and were discharged, while 113 sadly passed away. Statistically significant differences (p 0.05) were found between the recovered and deceased groups regarding several clinical parameters, including age, gender, mechanical ventilation duration, oxygen saturation, and various scoring systems (SOFA, APACHE II, GCS). In the second phase, the study employed a Naïve Bayes classifier using Python and the scikit-learn package to develop an AI model. The analysis revealed strong correlations between recovery or mortality and factors like age, bilirubin levels, and the receipt of specific corticosteroids. The model demonstrated an accuracy of over 73% in predicting patient outcomes, and the area under the ROC curve reached 0.81, indicating effective predictive performance. In conclusion, the study identified critical parameters influencing COVID-19 patient outcomes, validating these findings through AI analysis. The results are consistent with previous research and highlight the potential of AI in predicting recovery and mortality, underscoring its importance in clinical decision-making during respiratory crises associated with COVID-19.
کلمات کلیدی
Naïve Bayes algorithm, Machine Learning, Covid-19