Artificial intelligence Applications in Toxicoinformatics
Code: G-1212
Authors: Parisa ShoaeHagh * ℗
Schedule: Not Scheduled!
Tag: Biomedical Signal Processing
Download: Download Poster
Abstract:
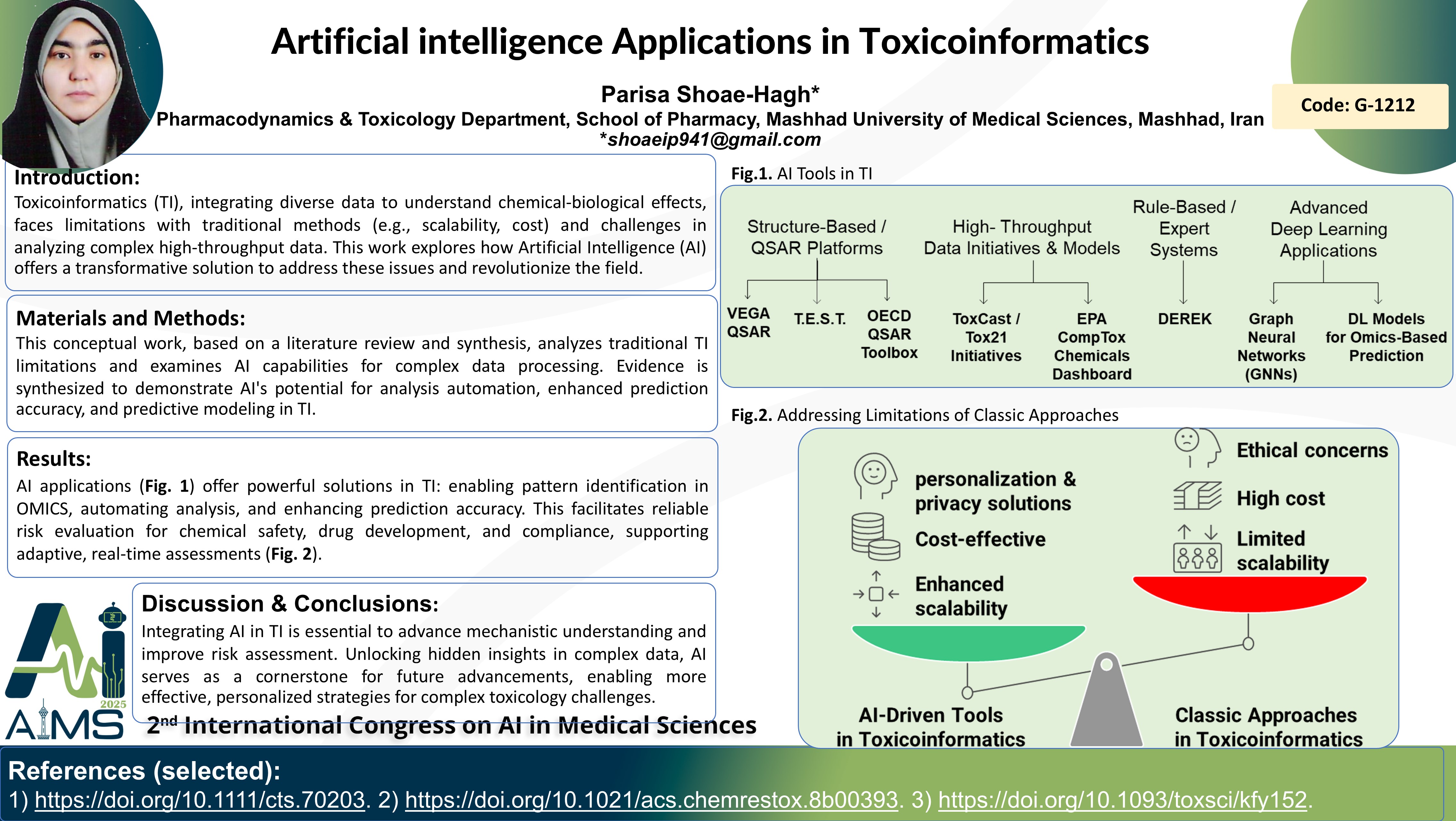
Abstract
This paper explores the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on toxicoinformatics, a field crucial for understanding the effects of chemicals on biological systems. Toxicoinformatics integrates diverse data types, including OMICS data (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics), to model complex biological responses to chemical exposures. Traditional toxicological evaluations, relying on in vivo and in vitro methods, face limitations in scalability, cost, and ethical considerations. The advent of high-throughput technologies like next-generation sequencing (NGS) has generated vast datasets, demanding sophisticated analytical approaches. This paper argues that AI, particularly machine learning and deep learning, offers powerful solutions to address these challenges. AI algorithms excel at identifying complex patterns and correlations within heterogeneous datasets, automating analytical processes, and enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of toxicity predictions. This capability is essential for rapid decision-making in drug development, chemical safety assessments, and regulatory compliance. Moreover, AI enables predictive modeling by integrating diverse data modalities, from chemical structures to genomic information, facilitating the development of sophisticated models capable of predicting toxicological endpoints. This is particularly relevant to personalized medicine, where individual genetic and phenomic profiles influence susceptibility to toxic effects. AI-driven toxicoinformatics allows for more reliable predictions and the consideration of individual variability, tailoring risk evaluations to specific populations. The paper further discusses the crucial role of AI in addressing emerging challenges in toxicoinformatics, such as real-time risk assessment in response to dynamic chemical exposures and evolving regulatory demands. By enabling rapid adaptation to new datasets and environmental conditions, AI technologies facilitate more rigorous and efficient regulatory strategies. This paper emphasizes the necessity of AI integration in toxicoinformatics for advancing scientific understanding, improving risk assessment accuracy, and ultimately prioritizing human health and environmental safety in an increasingly complex chemical landscape. The potential of AI to unlock hidden insights within complex toxicological data positions it as a cornerstone for future advancements in the field, paving the way for more effective and personalized approaches to chemical safety and risk management.
Keywords
Toxicoinformatics, Artificial-Intelligence, Machine-Learning, Deep-learning, OMICS, Predictive-Toxicology